Lebanon has about 220 km of coastline, largely made up of sedimentary rocks, loose sands or gravel. A high percentage of the population live by the coast which suffers from a number of challenges including high levels of development. Rich in freshwater reserves, Lebanon is home to 16 perennial and 23 seasonal rivers. Coastal aquifers in Lebanon are mainly karstic in nature, and groundwater satisfies nearly 45% of the country’s total water needs.
The introduction of the Water-Food-Energy-Ecosystems (WEFE) Nexus approach under Child Project 2.2 and the preparation of an Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM)* Strategy for Lebanon under CP 2.1 are aimed at enhancing coastal zone management and assisting the country in identifying solutions and priority actions that promote environmental security and enhance access to critical resources.
Under Project “Mediterranean Coastal Zones: Water Security, Climate Resilience and Habitat Protection” (C.P 2.1 of the MedProgramme) an Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) Strategy for Lebanon* is prepared by UNEP PAP/RAC. Climate change adaptation approaches will be mainstreamed in ICZM planning (through the SCCF Project) in collaboration with Blue Plan.
Activities under Project "Mediterranean Coastal Zones: Integrated Coastal Zones: Water Security, Climate Resilience and Habitat Protection"
 Activities undertaken under CP 2.1 address water related issues, such as surface waters, aquifers and related ecosystems in the context of the ICZM planning, ensuring the implementation of the IWRM principles. The ICZM plan uses the Integrative Methodological Framework, a comprehensive, comprehensible, and operational methodology for the integrated and sustainable management of the Mediterranean ecosystems constituted by the coastal zones, river basins and coastal aquifers.
Activities undertaken under CP 2.1 address water related issues, such as surface waters, aquifers and related ecosystems in the context of the ICZM planning, ensuring the implementation of the IWRM principles. The ICZM plan uses the Integrative Methodological Framework, a comprehensive, comprehensible, and operational methodology for the integrated and sustainable management of the Mediterranean ecosystems constituted by the coastal zones, river basins and coastal aquifers.
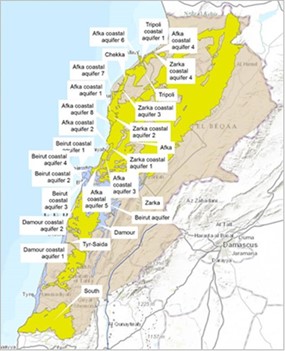
Map of main coastal lebanese aquifers
The Nexus approach (developed under CP 2.2) provides information about tradeoffs among the Water-Energy-Food-Ecosystems sectors in a source to sea context, thus taking into account upstreamcauses of specific challenges. Integrated Coastal Zone Planning in Lebanon (carried out by PAP/RAC) also integrates climate change adaptation and resilience efforts through the support of Plan Bleu/RAC.
Moreover, under CP 2.1 conjunctive surface water and groundwater management efforts are undertaken by UNESCO IHP in Lebanon, aiming to improve water supply reliability and sustainability, reduce groundwater over-extraction and land subsidence, improve or protect groundwater quality and environmental conditions. In this context, UNESCO IHP has carried out an assessment of the Damour coastal aquifer and related coastal ecosystems, including submarine groundwater discharges. The findings of this assessment inform the Integrated Management Plan for Damour, which is developed by all involved organizations in the framework of CP 2.1.
All of the above-mentioned activities support the effective implementation of laws and planning documents of the Lebanese Government, by addressing challenges that are geographically extending to the source-to-sea area.
SCCF: Special Climate Change Fund “Enhancing regional climate change adaptation in the Mediterranean Marine and Coastal Areas”.
*Lebanon ratified the ICZM Protocol in 2017.
For related activities see below links:
https://www.gwp.org/en/GWP-Mediterranean/WE-ACT/News-List-Page/2024/iczm-lebanon/
